摘要:本文介绍了Java容器类的核心接口,以及容器泛型的使用原则。
Abstract: This article describes the core interfaces of Java Collections, and the principles of using generic.
JDK java.util 包中包含了几个重要的集合类(主要包含实现了Collection接口和Map接口的类),从本篇文章开始总结JDK中自带的几个重要的容器类。
Java集合框架核心接口
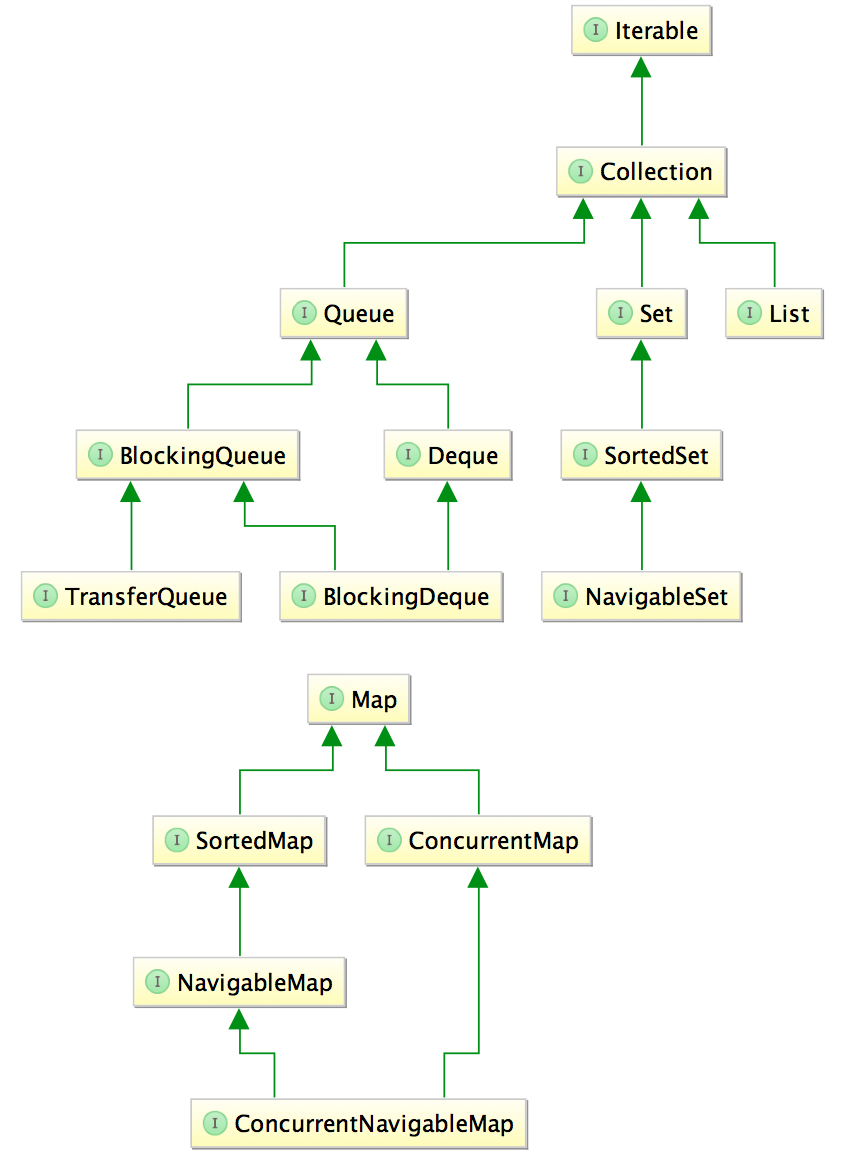
Iterable
实现了Iterable接口的类,可以使用foreach语法迭代,从JDK1.5开始加入。
package java.lang;
import java.util.Iterator;
public interface Iterable<T> {
/**
* Returns an iterator over a set of elements of type T.
*
* @return an Iterator.
*/
Iterator<T> iterator();
}
Collection
一组对象的集合。没有规定对象的顺序(如果有)和是否允许重复。Java平台不提供此接口的任何直接实现,但提供了更具体的子接口,如Set和List实现。
- 一般实现Collection子接口的类需要提供两个标准构造方法:1.无参构造方法(用于创建空集合)2.只有一个Collection类型参数的构造方法(用于创建一个集合副本)。这虽然不是硬性的规定(接口无法限定构造方法),但是每个实现类都遵循了这个原则。
- 对不支持的操作,应当抛出UnsupportedOperationException
public interface Collection<E> extends Iterable<E> {
// Query Operations
int size();
boolean isEmpty();
boolean contains(Object o);
Iterator<E> iterator(); //from Iterable
Object[] toArray();
<T> T[] toArray(T[] a);
// Modification Operations
boolean add(E e);
boolean remove(Object o);
// Bulk Operations
boolean containsAll(Collection<?> c);
boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c);
boolean removeAll(Collection<?> c);
boolean retainAll(Collection<?> c);
void clear();
// Comparison and hashing
boolean equals(Object o);
int hashCode();
}
这里引入一个小插曲:为什么Collection.add()方法使用了泛型,而remove()方法却使用了Object类型的参数?答案参见这里:
Why aren’t Java Collections remove methods generic?
Why does Set.contains() take an Object, not an E?
总结起来有以下几方面的原因:
- 当且仅当你需要防止Collection被破坏的时候,才考虑使用泛型约束
Actually, it’s very simple! If add() took a wrong object, it would break the collection. It would contain things it’s not supposed to! That is not the case for remove(), or contains(). Incidentally, that basic rule — using type parameters to prevent actual damage to the collection only — is followed absolutely consistently in the whole library. – Kevin Bourrillion
- 在remove上使用泛型限制,可能auto boxing问题
另外,泛型是编译期的静态类型检查,所以以下的泛型使用方式也是错误的:
List<? extends MinCut> list = new ArrayList<MinCut>();
这将导致除了null,list里不能插入任何对象。
Set
数学集合的抽象,不允许元素重复。
package java.util;
public interface Set<E> extends Collection<E> {
// Query Operations
int size();
boolean isEmpty();
boolean contains(Object o);
Object[] toArray();
<T> T[] toArray(T[] a);
// Modification Operations
boolean add(E e);
boolean remove(Object o);
// Bulk Operations
boolean containsAll(Collection<?> c);
boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c);
boolean retainAll(Collection<?> c);
boolean removeAll(Collection<?> c);
void clear();
// Comparison and hashing
boolean equals(Object o);
int hashCode();
}
SortedSet
有序对象集合。SortedSet中的对象会根据Comparable接口或提供的Comparator进行排序。
package java.util;
public interface SortedSet<E> extends Set<E> {
Comparator<? super E> comparator();
SortedSet<E> subSet(E fromElement, E toElement);
SortedSet<E> headSet(E toElement);
SortedSet<E> tailSet(E fromElement);
E first();
E last();
}
NavigableSet
继承SortedSet并且其中的元素可以按照升序和降序访问。
package java.util;
public interface SortedSet<E> extends Set<E> {
Comparator<? super E> comparator();
SortedSet<E> subSet(E fromElement, E toElement);
SortedSet<E> headSet(E toElement);
SortedSet<E> tailSet(E fromElement);
E first();
E last();
}
List
有序集合,也称为序列(Sequence)。一般情况下允许元素重复。允许按位置访问。
package java.util;
public interface List<E> extends Collection<E> {
// Query Operations
int size();
boolean isEmpty();
boolean contains(Object o);
Iterator<E> iterator();
Object[] toArray();
<T> T[] toArray(T[] a);
// Modification Operations
boolean add(E e);
boolean remove(Object o);
// Bulk Modification Operations
boolean containsAll(Collection<?> c);
boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c);
boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c);
boolean removeAll(Collection<?> c);
boolean retainAll(Collection<?> c);
void clear();
// Comparison and hashing
boolean equals(Object o);
int hashCode();
// Positional Access Operations
E get(int index);
E set(int index, E element);
void add(int index, E element);
E remove(int index);
// Search Operations
int indexOf(Object o);
int lastIndexOf(Object o);
// List Iterators
ListIterator<E> listIterator();
ListIterator<E> listIterator(int index);
// View
List<E> subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex);
}
Queue
专为保存加工前的元素的集合。除了基本的Collection操作,队列提供额外的插入、提取和检查操作。
public interface Queue<E> extends Collection<E> {
boolean add(E e);
boolean offer(E e);
E remove();
E poll();
E element();
E peek();
}
BlockingQueue
阻塞队列
package java.util.concurrent;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.Queue;
public interface BlockingQueue<E> extends Queue<E> {
boolean add(E e);
boolean offer(E e);
void put(E e) throws InterruptedException;
boolean offer(E e, long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
throws InterruptedException;
E take() throws InterruptedException;
E poll(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
throws InterruptedException;
int remainingCapacity();
boolean remove(Object o);
public boolean contains(Object o);
int drainTo(Collection<? super E> c);
int drainTo(Collection<? super E> c, int maxElements);
}
TransferQueue
生产者可以等待消费者接收元素的阻塞队列。
package java.util.concurrent;
public interface TransferQueue<E> extends BlockingQueue<E> {
boolean tryTransfer(E e);
void transfer(E e) throws InterruptedException;
boolean tryTransfer(E e, long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
throws InterruptedException;
boolean hasWaitingConsumer();
int getWaitingConsumerCount();
}
Deque
双端队列,支持在两端插入和删除元素。扩展了Queue接口。
package java.util;
public interface Deque<E> extends Queue<E> {
void addFirst(E e);
void addLast(E e);
boolean offerFirst(E e);
boolean offerLast(E e);
E removeFirst();
E removeLast();
E pollFirst();
E pollLast();
E getFirst();
E getLast();
E peekFirst();
E peekLast();
boolean removeFirstOccurrence(Object o);
boolean removeLastOccurrence(Object o);
// *** Queue methods ***
boolean add(E e);
boolean offer(E e);
E remove();
E poll();
E element();
E peek();
// *** Stack methods ***
void push(E e);
E pop();
// *** Collection methods ***
boolean remove(Object o);
boolean contains(Object o);
public int size();
Iterator<E> iterator();
Iterator<E> descendingIterator();
}
BlockingDeque
阻塞双端队列
Map
键值映射,每个键对应一个值。
SortedMap
按Key有序的Map
NavigableMap
继承SortedMap,并且其中的元素可以按照Key升序和降序访问。
ConcurrentMap
putIfAbsent、remove和replace方法都具有原子性.
ConcurrentNavigableMap
元素可以按照Key升序和降序访问。